New Automobile Invention You Should Know
The automobile industry constantly changes, with new technologies and innovations emerging every year. Many new technologies are being developed to alter how we use and think about cars. In 2022, we can expect significant changes in the way vehicles are designed and operated. John Lee's Panama City Mazda will discuss the ten car technologies that will change the automobile industry in 2023
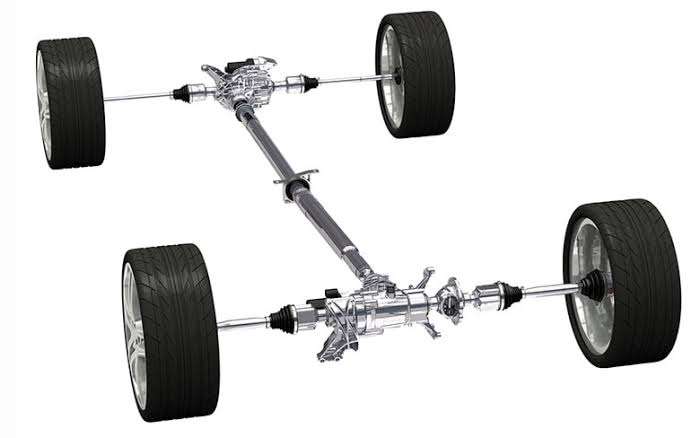
1. INTELLIGENT ALL-WHEEL DRIVE
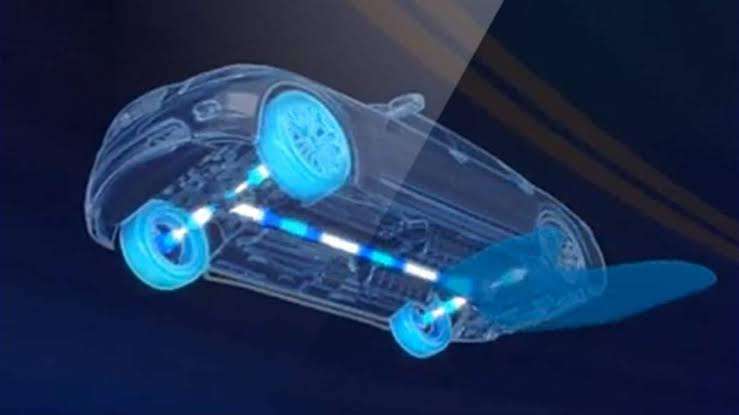
It is a new type of all-wheel-drive system that uses sensors to monitor each wheel's traction constantly. If a wheel starts to slip, the system will automatically send more power to that wheel to maintain traction.
Intelligent AWD Overview:
Intelligent All-Wheel Drive (AWD) refers to a sophisticated system that actively monitors driving conditions and distributes power to the wheels in a manner that optimizes traction and stability. While I can provide a general understanding of Intelligent AWD, it's important to note that specific implementations and technologies may vary among different vehicle manufacturers.
Intelligent AWD systems typically utilize sensors, control modules, and various algorithms to constantly monitor factors such as wheel speed, throttle input, steering angle, lateral acceleration, and road conditions. Based on this information, the system can dynamically adjust the power distribution between the front and rear wheels to provide enhanced traction and control.
When the system detects a loss of traction or slip on one or more wheels, it can transfer torque to the wheels with better grip, helping to improve traction and maintain stability. This proactive power distribution can be particularly beneficial in adverse weather conditions, such as rain, snow, or ice, where maintaining control of the vehicle is crucial.
Some Intelligent AWD systems also incorporate additional features such as torque vectoring. Torque vectoring allows the system to selectively distribute power to individual wheels or even vary the power between the left and right wheels. This capability can enhance cornering performance, stability, and agility by providing additional power to the outer wheels during turns, helping the vehicle rotate more efficiently.
It's worth noting that the specific capabilities and performance of Intelligent AWD systems may vary depending on the vehicle and manufacturer. Different manufacturers may have their own unique branding and names for their intelligent AWD technologies, such as Subaru's Symmetrical All-Wheel Drive or Audi's Quattro system, which incorporate their own specific engineering and design approaches.
2. ACTIVE AERODYNAMICS:
Active aerodynamics is a new technology that allows cars to adjust their aerodynamic properties. It can improve fuel efficiency and performance and make the car more stable in high winds.
The primary goal of active aerodynamics is to improve the vehicle's overall efficiency, stabil
There are several common examples of active aerodynamics used in different types of vehicles:
Adjustable rear spoiler: Many high-performance sports cars feature rear spoilers that can be raised or lowered to optimize downforce and reduce drag depending on the driving conditions. The spoiler adjusts its position based on factors like vehicle speed, throttle input, and braking forces.
Active grille shutters: These are found in some modern cars and trucks. The grille shutters can open or close to regulate the airflow through the radiator and engine compartment. By closing the shutters at high speeds, the aerodynamic drag is reduced, leading to improved fuel efficiency. The shutters can open when the engine requires more cooling or during low-speed driving conditions.
Dynamic air intakes: Some high-performance vehicles incorporate adjustable air intakes that can open or close to control the airflow into the engine. These intakes can optimize the air supply based on factors like engine temperature, speed, and power demand, enhancing performance and efficiency.
Active suspension systems: While not directly related to aerodynamics, active suspension systems can contribute to improved aerodynamic performance. These systems can adjust the ride height of the vehicle based on the driving conditions, lowering the vehicle at higher speeds to reduce drag and increase stability.
3.AUGMENTED REALITY WINDSHIELDS
Augmented reality windshields are among the car technologies gaining popularity in luxury cars. These windshields use a video camera and head-up display to project information onto the windshield, such as turn-by-turn directions or speed limits.
4. AUTONOMOUS EMERGENCY BRAKING
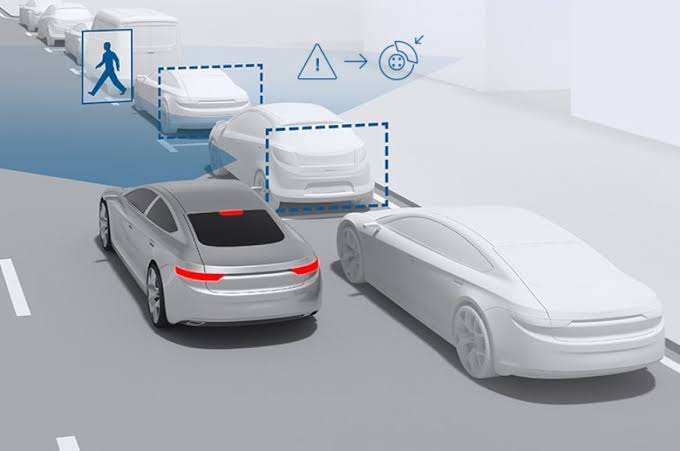
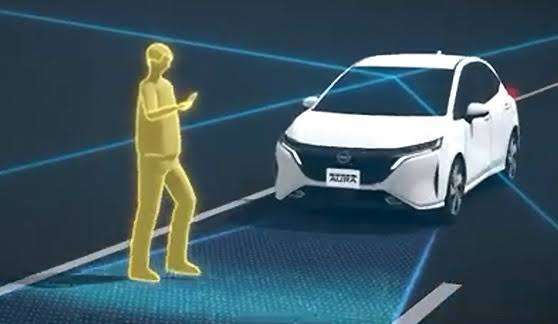
Autonomous emergency braking is a safety feature that uses sensors to detect when a car is about to collide with another object. Automatic brakes reduce the severity of a collision.
Auto Emergency Braking (AEB)
Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB), also known as Automatic Emergency Braking or Collision Avoidance System, is an advanced safety feature found in many modern vehicles. AEB is designed to assist drivers in avoiding or mitigating collisions with other vehicles, pedestrians, or obstacles on the road.
The primary function of AEB is to detect potential collision risks and intervene by applying the brakes automatically if the driver fails to respond in a timely manner. It uses a combination of sensors, such as radar, cameras, and sometimes lidar, to monitor the road ahead and assess the distance and relative speed of objects in front of the vehicle.
When the AEB system detects an imminent collision, it typically issues a warning to the driver, usually through visual or auditory alerts, to prompt them to take evasive action. If the driver does not respond or fails to apply sufficient braking force, the AEB system will automatically engage the brakes to either prevent the collision or reduce its severity.
There are generally two types of AEB systems:
Forward Collision Warning (FCW) with AEB: This system provides a warning to the driver when a potential collision is detected, but it does not actively apply the brakes. It alerts the driver to take action and provides additional time to react and avoid the collision.
Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB): This system not only warns the driver of an impending collision but also initiates automatic braking if the driver does not respond in time. It can apply full or partial braking force to reduce the impact speed or bring the vehicle to a complete stop, depending on the situation.
AEB systems can greatly enhance safety on the roads by reducing the risk of front-end collisions, especially in situations where the driver may be distracted, fatigued, or unable to react quickly enough. It is worth noting that while AEB is a valuable safety feature, it is not a substitute for attentive and responsible driving. Drivers should always remain focused and ready to intervene when necessary, even with advanced safety technol
ogies in place.
5. CONNECTED CARS
Connected cars are equipped with internet connectivity, allowing them to communicate with other connected vehicles and devices. It can provide information on traffic conditions, weather, and more.
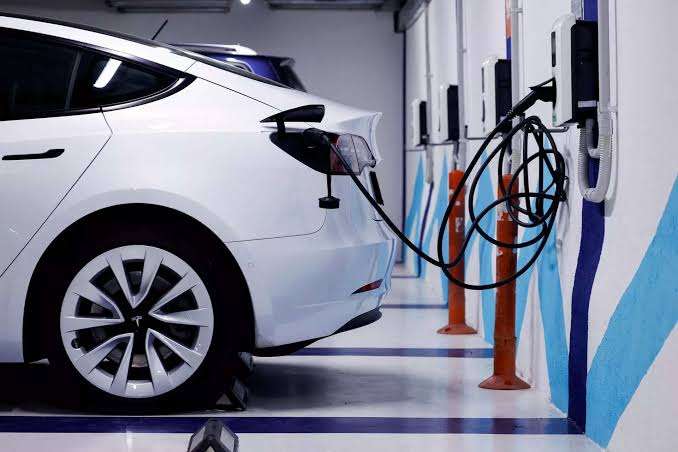
6. ELECTRIC VEHICLES:
Electric vehicles are powered by electricity instead of gasoline or diesel. They are getting popular due to their environmental benefits and lower operating costs.
EVs: Benefits, Technology, Adoption
Electric vehicles (EVs) are vehicles that are powered by electricity stored in onboard batteries, rather than relying on traditional internal combustion engines (ICE) that use fossil fuels. EVs have gained significant popularity in recent years due to their environmental benefits and advancements in battery technology. Here are some key points about electric vehicles:
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs):
These vehicles run entirely on electricity and do not have a combustion engine. They are powered by rechargeable batteries and produce zero tailpipe emissions.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs):
PHEVs combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine. They can be charged using an external power source, and they also have a gasoline engine that can provide additional range when the battery is depleted.
Environmental Benefits: EVs contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution since they produce zero tailpipe emissions. However, the overall environmental impact depends on how the electricity used to charge them is generated. If the electricity comes from renewable sources, the environmental benefits are maximized.
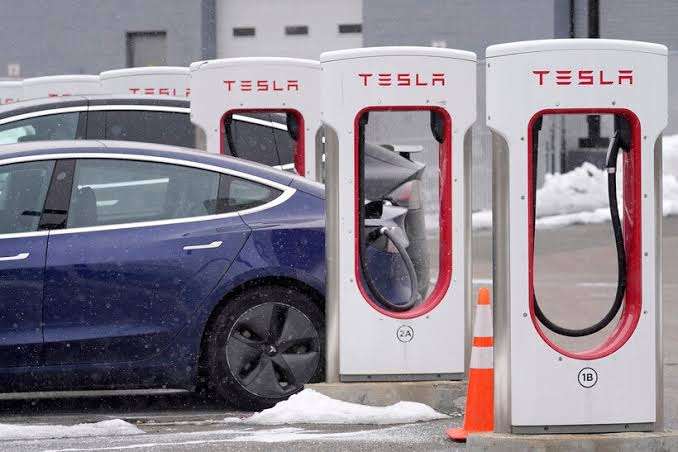
Range and Charging: EVs have improved significantly in terms of range, with some models capable of traveling over 300 miles (480 kilometers) on a single charge. However, range can vary depending on factors such as driving conditions and weather. Charging an EV can be done at home using a standard power outlet or a dedicated charging station, and there is also an increasing number of public charging stations available.
Cost: Electric vehicles generally have a higher upfront cost compared to conventional vehicles due to the cost of batteries. However, they can provide long-term cost savings in terms of fuel and maintenance. The cost of EVs and their batteries has been decreasing over time as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved.
GovernmentIncentives: Many governments around the world offer incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, and grants that make EVs more affordable for consumers.
Infrastructure Development: As the popularity of electric vehicles grows, there is an increasing focus on expanding charging infrastructure. Governments, businesses, and utility companies are investing in the installation of charging stations in public spaces, workplaces, and residential areas to support the widespread adoption of EVs.
It's important to note that my knowledge cutoff is in September 2021, so there may have been further advancements and developments in electric vehicle technology since then.
7. FUEL CELLS
Fuel cells are an alternative to battery-powered electric vehicles. They convert chemical energy into electrical energy, which can then power an electric motor.
8. SELF-DRIVING CARS
Self-driving cars are the ultimate vision of upcoming car technologies. They are equipped with sensors and software to navigate without human input. They are still in development, but many believe they will become commonplace on our roads.
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, are vehicles that can operate without human intervention. These vehicles use a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and advanced artificial intelligence algorithms to perceive the environment, make decisions, and navigate on their own.
The development of self-driving cars has been a topic of significant interest and investment in recent years. Many technology and automotive companies, such as Tesla, Waymo (owned by Alphabet Inc.), Uber, and General Motors, have been actively working on autonomous vehicle technology.
There are different levels of autonomy in self-driving cars, categorized by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). These levels range from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation), with each level representing the extent of human involvement required in the driving process.
Currently, most commercially available self-driving cars are at Level 2 or Level 3, which means they can handle some driving tasks under certain conditions but still require human supervision. These systems are often referred to as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
The transition to fully autonomous Level 4 or Level 5 vehicles, where human intervention is not necessary in most driving situations, is still under development and faces various technological, regulatory, and ethical challenges. However, significant progress has been made in the field, and several self-driving car prototypes have undergone successful testing in various environments.
The potential benefits of self-driving cars include improved road safety, reduced traffic congestion, increased mobility for individuals who cannot drive (such as the elderly or disabled), and potential environmental benefits through optimized driving patterns.
9. CAR SHARING
Car sharing service allows people to rent cars by the hour or day. It is often seen as a more sustainable and convenient alternative to owning a car. It surpasses the added costs of car ownership or leasing & allows responsible users the opportunity to travel with ease on the basis of a shared schedule.
10. IN-CAR ENTERTAINMENT
In-car entertainment systems provide passengers with entertainment options while traveling in a car. They often include music streaming, video streaming, and social media integration.